
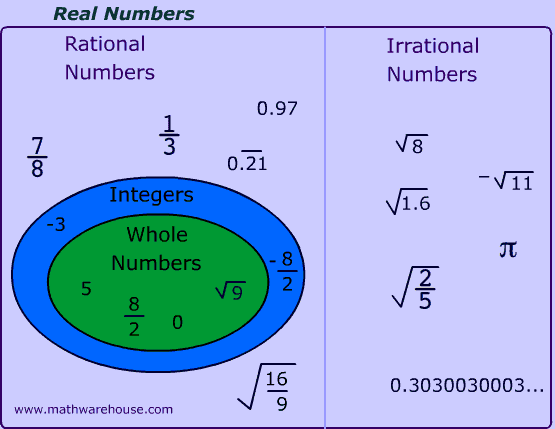
Other words, by adding a number to its negative or opposite, theĮvery point of the number line corresponds to one real number. There are natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers and real numbers. Remember that all the counting numbers and all the whole. There is a unique real number, denoted − x , Since any integer can be written as the ratio of two integers, all integers are rational numbers. Is between 0 and 1 including the endpoints.Ĭorresponds to the point A' which is symmetrical regarding the origin to the point | + 5 | = 5 and | − 5 | = 5, and 0 is the only absolute value of 0. The absolute value (or modulus) of a real numberĭenoted | x | is its numerical value without regard to its sign. Therefore it can be said that integers are rational, irrational, natural and whole numbers are subsets of real numbers. This case the number line is called the x -axis. To denote a one-dimensional coordinate system, in The real number line is an infinite line on which points are taken to represent the real numbers by their distance from a fixed point labeled With the points on an infinite line, the number line. Irrational and are intuitively defined as numbers that are in one-to-one correspondence The real numbers or the reals are either rational or The set of all rational and irrational numbers, R = Ö 2, Ö 3, or any root of any natural number that is not a perfect root is an irrational number. Irrational numbers, denoted I, is the set of numbers thatĬannot be written as ratio of two integers.Īn irrational number expressed as a decimal never repeat or terminate. The irrational numbers are precisely those numbers whose decimal expansion never ends and never entersĪ periodic pattern, such as 0.1020030004., p , Rational numbers can be represented as integers, fractions, terminating decimals and recurring or repeating decimals. The values a and b can be zero, so the set of real numbers and the set of imaginary numbers are subsets of the set of complex numbers. These are all the rational numbers (including natural numbers, whole numbers, and integers) and all the irrational numbers. That is, a ratio orĪll integers are in this set since every integer aĪnd the set of integers is proper subset of the set of rational A combination of a real and an imaginary number in the form a + bi, where a and b are real, and i is imaginary. Is not 0 }, is the set of all proper and improper fractions. This means that the set of natural numbers is a subset of }, consists of all natural numbers, negative whole numbers and }, is just like the set of natural numbers except that it alsoĠ, 1, 2, 3. Natural numbers are all of the counting numbers. }, the positive integers used for counting. Real numbers consist of rational numbers, integers, whole numbers, natural or counting numbers, and irrational numbers. Set of Real Numbers - The Real Number System


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
